What Is Parallel Execution?
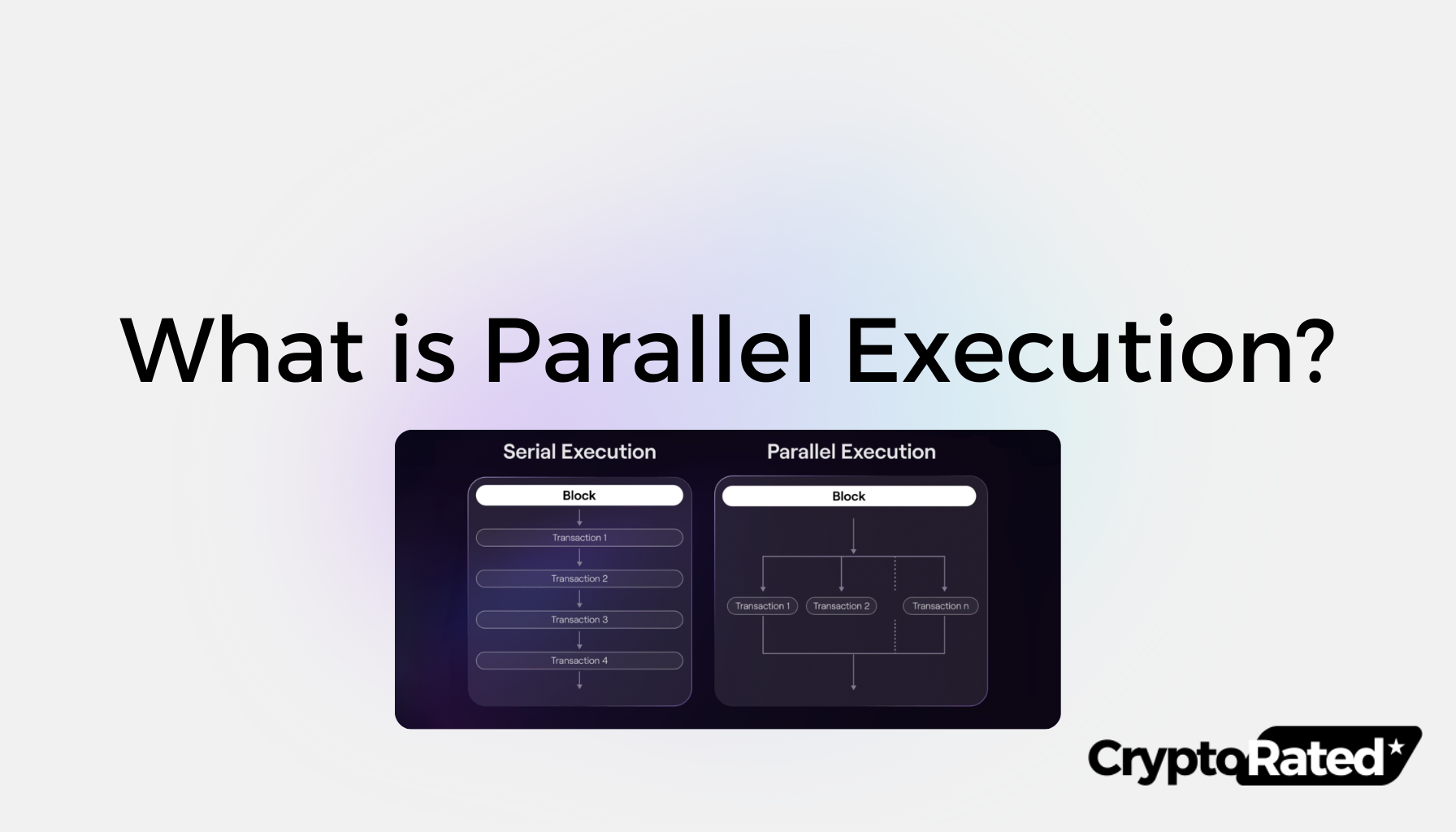
In the realm of blockchain technology, parallel execution has emerged as a transformative solution that aligns with the ever-growing demand for speed and expanded capabilities. By allowing multiple transactions to flow simultaneously, this approach significantly enhances network efficiency.
Blockchains harnessing this technology, including leaders like Solana with its Sealevel system1, have redefined expectations with impressive transaction processing velocities, which have cascaded into a boom in decentralized application (dApp) development. Despite bolstering the performance with transaction speeds reaching up to 1000 transactions per second (TPS), these systems underscore the delicate balance between speed and maintaining the grassroots principle of decentralization.
Key Takeaways
- Parallel execution enhances blockchains by allowing simultaneous transactions, improving scalability.
- Blockchain systems utilizing parallel execution, such as Solana’s Sealevel, reach remarkable transaction speeds.
- While parallel execution improves network efficiency, it also must address the challenges of complexity and decentralization.
What Are Parallel Executions in Blockchain Technology?
Parallel execution in blockchain technology significantly enhances the capacity to manage numerous transactions at once. This diverges from the traditional approach of handling one transaction after another. By processing multiple transactions concurrently, the network can alleviate bottlenecks and accelerate transaction completion, thus elevating the user experience during times of high demand.
Key Benefits:
- Increased throughput: Multi-transaction processing power enhances network efficiency2.
- Improved scalability: Supports more transactions, enabling growth within decentralized networks.
- User experience: Reduces transaction confirmation times.
While parallel execution expands the capabilities of blockchain networks to facilitate a higher number of transactions, it also involves the complexities of coordinating updates across various nodes, which must be carefully balanced against the fundamental principle of decentralization.
Some Examples of Parallel Transaction Processing in Blockchain Networks
Blockchains employing parallel processing methodologies have significantly improved their transactional capabilities and scalability. They include:
- Sei: This blockchain focuses on exchanges of digital assets, ensuring rapid processing through its advanced architecture designed for speed. Dual consensus mechanisms and market-oriented parallelization deliver an optimized experience for exchange applications.
- Sui: By processing transactions in parallel, Sui has amplified its throughput. The simultaneous management of states aids in maintaining consistency after transactions, positioning Sui at the forefront of blockchain efficiency.
- Aptos: Aptos stands out for its concurrent transaction processing, leveraging snapshot-based methods. These techniques mark a stride in addressing the limits of sequential processing, enhancing the Aptos network’s capacity to handle transactions.
- Solana: With its Sealevel technology, Solana excels in executing transactions across several nodes at once. This leads to significantly reduced wait times for transaction confirmations and cements Solana’s status as a swift and reliable blockchain.
These platforms collectively illustrate the diverse implementations and advantages of parallel processing in blockchains, highlighting its role in augmenting the sector’s proficiency in dealing with digital transactions.
How Does Parallel Execution Work?
Parallel processing within blockchain networks enables the simultaneous execution of distinct transactions. This approach moves away from linear processing to improve both speed and scalability.
- Selection of Non-conflicting Transactions: Initially, the system filters out transactions that can operate independently—ones that don’t share data or affect the same digital ledger state. For instance, distinct smart contracts in some networks can be processed concurrently3.
- Simultaneous Transaction Processing: After differentiating these transactions, they proceed to run collectively across multiple nodes in the network. This method substantially shortens the time needed to confirm transactions, leveraging technologies resembling those used by Solana’s Sealevel framework.
- Conflict and Dependency Management: As transactions are processed, the system must also navigate any interdependencies or conflicts that arise, applying solutions to uphold the accuracy and consistency of the blockchain data.
What Are Some of the Issues with Parallel Execution?
While parallel execution can enhance the scalability and efficiency of blockchain systems, it brings its own set of issues:
- Resource Strain: Handling numerous transactions at once can overburden network resources, particularly affecting nodes responsible for quick updates and validation of transactional statuses.
- Increased Complexity: A higher level of complexity in transaction management and coordination may contribute to the emergence of errors and heighten security risks.
- Decentralization Impact: The intrinsic design complexity due to parallelization efforts might influence the decentralized essence of the blockchain.
These challenges must be carefully weighed against the potential performance gains by blockchain developers and the user community.
Final Thoughts on Parallel Executions In Crypto
Parallel execution has emerged as a game-changer in the realm of blockchain technology, offering a transformative solution for enhancing network efficiency and transaction processing speeds. By enabling simultaneous execution of multiple transactions, parallel processing has revolutionized blockchain infrastructure, propelling platforms like Solana and Aptos to the forefront of scalability and performance.
While this innovation has revolutionized the industry, it also brings forth complexities in transaction management and network design. Careful consideration of these challenges is paramount as the blockchain community navigates the path towards a future of seamless, high-throughput blockchains.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is parallel execution in blockchains?
Parallel execution is a technique that allows blockchains to process multiple transactions simultaneously rather than processing them one at a time. This can significantly improve the speed and scalability of blockchains.
-
What are the benefits of parallel execution in blockchains?
Parallel execution offers several advantages for blockchains, including:
Increased throughput: Parallel processing can enable blockchains to handle a much higher volume of transactions per second.
Improved scalability: Parallel execution makes blockchains more scalable, enabling them to accommodate growing user bases and transaction volumes without performance bottlenecks.
Reduced latency: Parallel processing reduces transaction confirmation times, providing users with quicker transaction finalization.
-
What are the challenges of parallel execution in blockchains?
Implementing parallel execution poses a few challenges, including:
Increased complexity: Designing and maintaining parallel blockchain systems is more complex, posing challenges in ensuring system security and correctness.
Resource strain: Parallel processing can place significant demands on the resources of blockchain nodes, potentially reducing overall network throughput.
Decentralization concerns: Parallel execution could impact the decentralized nature of blockchains, potentially concentrating power among certain nodes.
WRITTEN
Peter Barker
Peter is an experienced crypto content writer and a DeFi enthusiast with more than 3+ years of experience in the space. Previously a journalist and news editor at a leading European news sourcing agency.




